2020-8-4 04:38 |
Ethereum has been putting its foot to the pedal over the last two months, generating new record-breaking usage numbers that paint apparent demand for the platform. Can the network keep up?
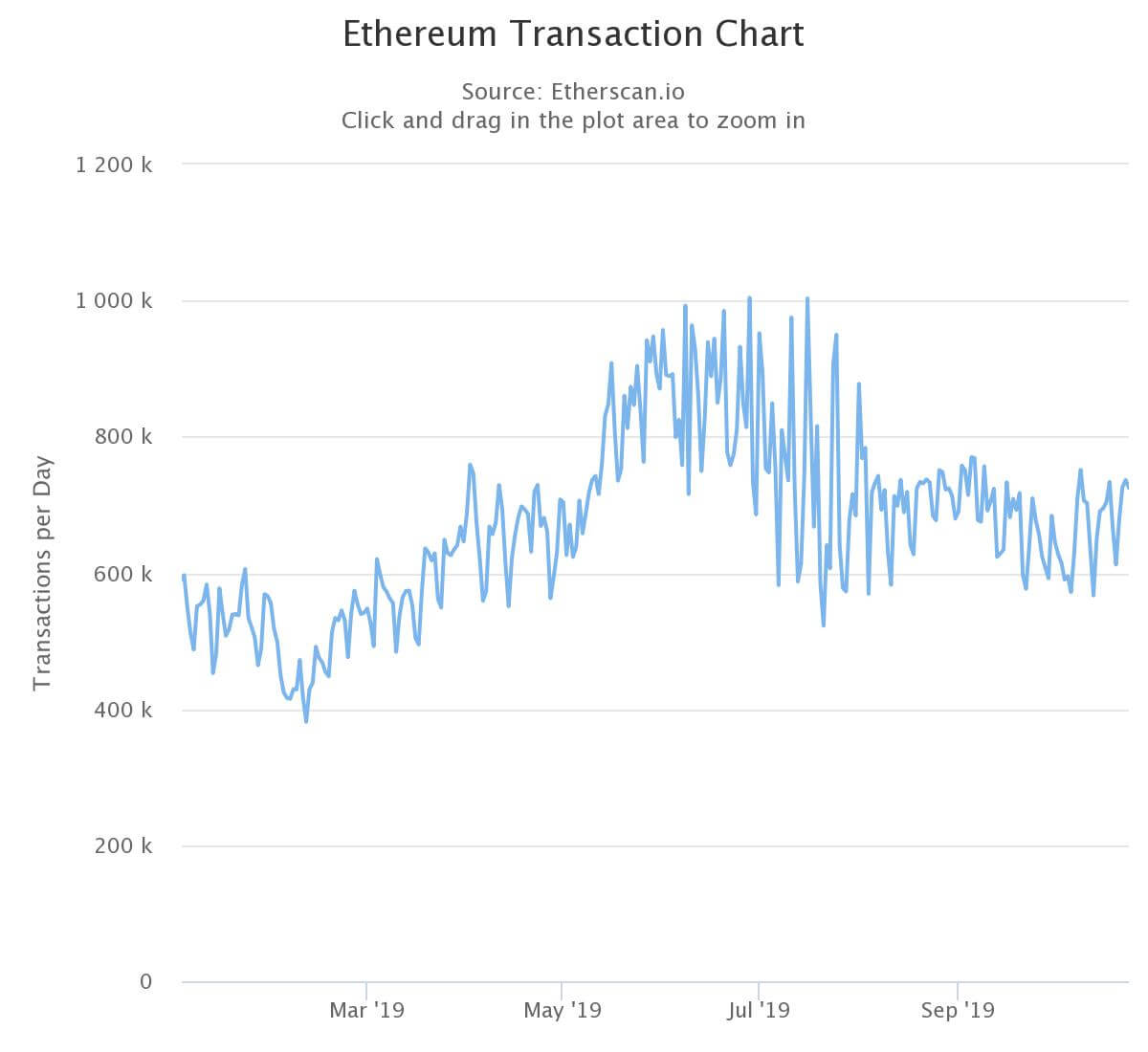
Source: Etherscan.ioEthereum enthusiasts will be quick to attribute this achievement to DeFi protocols like Uniswap, Compound, and yEarn—and the imminent launch of the ETH 2.0’s testnet. They are undoubtedly part of the higher activity numbers, but they are not the principal reason behind ETH’s network congestion.
Much of the responsibility lies with Ponzi schemes Forsage, MMM, and Lion’s Share. Based on the total number of transactions and standard gas limits for the contracts, these scam smart contracts were responsible for approximately 5,600 ETH in gas fees over the last month, or about 10% of total consumption.
To put this in perspective, in terms of network usage this would put these three Ponzis on par with Tether, which conducts tens of millions of transactions and moves billions of dollars over Ethereum.
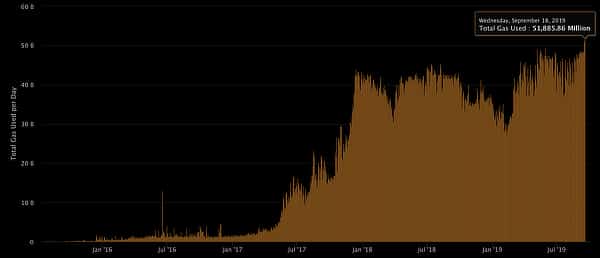
Since mid-July, Ethereum has facilitated at least 1 million transactions every day at the cost of 21 billion gas. Excluding simple transactions, 57 billion is used exclusively for smart contracts. Ponzi schemes comprise about 17 billion of this consumption, almost 30% of smart contract activity.
As a result of these scams, gas prices are inflated, floating between 35 and 90 gwei. In real terms, this is already showing in average transaction prices. A typical Ethereum transaction currently costs about $2, highs not seen since the middle of 2018. Though fast-climbing ETH prices are partially responsible.
Nonetheless, Ethereum is working on implementing a scaling solution, ETH 2.0, to help address the load associated with growing adoption of the network.
origin »Ethereum (ETH) на Currencies.ru
|
|